Introduction
Scantron’s is a globally recognized system that has transformed the way tests, assessments, and surveys are conducted. At its core, Scantron relies on machine-readable forms paired with Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) technology, allowing it to quickly and accurately capture responses marked on specially designed forms. This technology eliminates much of the manual effort traditionally required in grading, making it an essential tool in educational institutions, corporate environments, and research organizations.
The system works by having respondents fill in designated areas—typically bubbles or checkboxes—on Scantron forms using a pencil or pen. Once completed, these forms are processed through Scantron machines or scanners, which detect the marks and convert them into digital data for scoring or analysis. This not only saves a significant amount of time compared to manual grading but also ensures a high level of accuracy, minimizing human error.
Scantron’s widespread adoption is due to its versatility. In schools and universities, it is commonly used for multiple-choice exams, standardized tests, and quizzes, providing educators with fast, reliable results. Beyond education, businesses and organizations employ Scantron for surveys, evaluations, and feedback collection, where quick and precise data processing is crucial. By combining simplicity with advanced technology, Scantron has become a trusted solution for efficiently managing large-scale assessments and data collection.
History
Scantron Corporation was founded in 1972 in the United States, during a period when educational institutions were seeking more efficient ways to handle the growing volume of standardized testing. The company’s primary goal was to automate the grading process for schools and universities, significantly reducing the time, effort, and errors associated with manually scoring multiple-choice exams. Prior to Scantron, teachers and administrators faced labor-intensive grading processes that were prone to mistakes, especially in large classrooms or during standardized assessments.
The invention of optical mark recognition (OMR) technology became the backbone of Scantron’s success. This technology allowed computers to read marked forms quickly and accurately, transforming the way schools managed testing and evaluation. The system’s reliability and speed quickly earned it widespread adoption across educational institutions in the United States and eventually worldwide.
As Scantron grew, its applications expanded beyond education. The company began offering solutions for surveys, assessments, and data collection in corporate, government, and research settings. This expansion allowed organizations to gather large amounts of data efficiently, analyze results accurately, and make informed decisions based on the insights collected. Today, Scantron is recognized not only for its contributions to automated testing but also as a leader in data collection and assessment solutions, serving a diverse range of industries beyond its original educational focus.
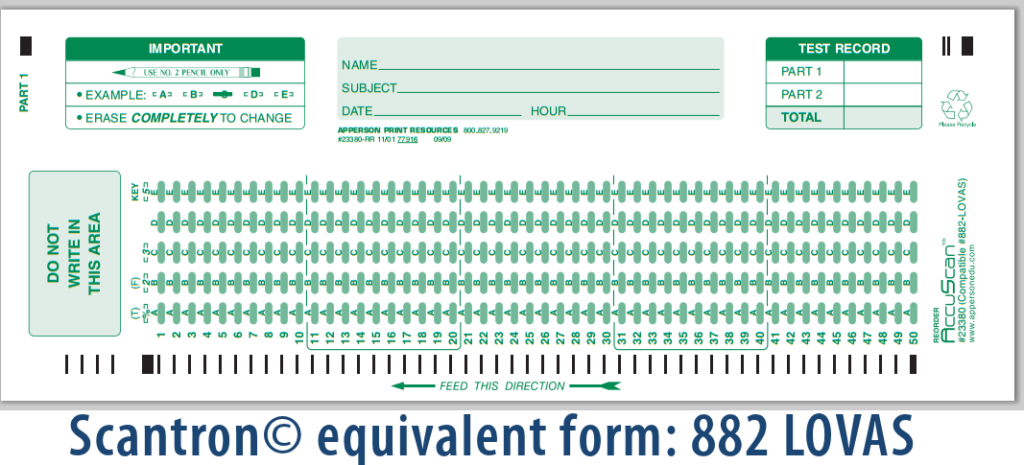
How Scantron Works
Scantron operates on a combination of specially designed forms and optical mark recognition (OMR) technology, which together enable the automated collection and processing of responses with remarkable speed and accuracy. The system’s workflow is simple in concept but highly efficient in execution, making it indispensable in large-scale testing and survey scenarios.
- Form Design: The process begins with the creation of Scantron forms, which are pre-printed with rows of bubbles or checkboxes corresponding to questions or survey options. These forms are carefully structured to ensure compatibility with OMR scanners, with precise spacing and alignment to allow accurate detection of marks. Forms can vary depending on the type of assessment, ranging from multiple-choice exams to survey questionnaires.
- Filling Out Responses: Respondents use a pencil (usually No. 2) to fill in their answers completely within the designated bubbles. The choice of pencil is critical because it creates a mark that is easily detectable by the OMR scanner. It is also important that marks are filled in clearly and within the boundaries to avoid errors during scanning.
- Scanning and Detection: Once completed, the forms are fed into a Scantron machine or compatible OMR scanner. The scanner uses light to detect the presence of marks in predetermined locations. Areas that are filled in reflect differently than blank spaces, allowing the machine to accurately capture the selected responses. Advanced Scantron systems can process hundreds or even thousands of forms per hour, making them ideal for large classrooms or mass surveys.
- Data Processing: After scanning, the responses are compiled into digital data. Scantron software automatically grades multiple-choice tests according to an answer key, calculates scores, and generates detailed reports. For surveys or feedback forms, the software can analyze trends, tally responses, and produce visual summaries such as charts and graphs.
- Accuracy and Efficiency: One of Scantron’s greatest strengths lies in its high accuracy. By reducing human involvement in grading, the system minimizes errors, ensures consistency, and saves significant amounts of time. Its reliability has made it a trusted solution for educational institutions, certification boards, and businesses worldwide.
By combining precise form design, careful response marking, and sophisticated scanning technology, Scantron provides an automated system that transforms large-scale testing and data collection into a fast, accurate, and efficient process.
Key Technology
At the heart of Scantron’s efficiency and reliability lies its key technology, primarily Optical Mark Recognition (OMR). This technology is what allows Scantron to automatically capture and process responses with high speed and precision, setting it apart from traditional manual grading methods.
1. Optical Mark Recognition (OMR):
OMR is a method used to detect the presence of marks in predetermined areas on a Scantron form. When a respondent fills in a bubble or checkbox, the OMR scanner identifies these marks by shining a light on the form and measuring the reflection. Filled-in areas reflect light differently than blank spaces, enabling the scanner to detect the selections accurately. This process allows hundreds or even thousands of responses to be recorded in a fraction of the time it would take to grade manually. The technology is highly reliable as it is designed specifically to read marks made within precise boundaries, reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
2. Accuracy and Efficiency:
Scantron’s OMR technology ensures high precision and minimal human error. Unlike manual grading, which can be inconsistent or slow, Scantron can process large volumes of forms in minutes while maintaining consistent results. Its efficiency is particularly valuable for standardized testing, certification exams, and large-scale surveys, where the accuracy of results is critical. Furthermore, by automating the scoring process, educators, businesses, and researchers can focus more on analyzing data rather than spending excessive time on data collection and grading.
In essence, Scantron’s success is built on the seamless integration of OMR technology with software capable of rapidly processing and interpreting responses. This combination makes Scantron a trusted tool for reliable, large-scale assessment and data collection worldwide.
Types of Scantron Forms
Scantron provides a range of forms tailored to serve the varied requirements of educational institutions, businesses, and research organizations. Each type of form is tailored for specific purposes, yet all are compatible with Scantron’s Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) technology, ensuring fast and accurate data collection.
1. Educational Test Forms:
These are the most common Scantron forms and are primarily used in schools, colleges, and universities. They are designed for multiple-choice exams, quizzes, and standardized tests. Students fill in bubbles corresponding to their answers, and the forms are scanned to produce immediate results. These forms help educators save time while maintaining consistent grading standards across large classes.
2. Surveys and Feedback Forms:
Scantron forms are widely used for employee evaluations, customer satisfaction surveys, and market research. Organizations can collect large volumes of feedback efficiently, and the data can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. These forms are particularly valuable for gathering structured responses quickly and systematically.
3. Attendance and Registration Forms:
Scantron also provides forms for administrative purposes, such as tracking attendance, registering participants for events, or recording membership information. By using OMR scanning, these forms enable fast processing of participant information, reducing paperwork and manual data entry.
4. Custom and Specialized Forms:
In addition to standard educational and survey forms, Scantron offers customizable forms that can be adapted for unique testing or data collection needs. Organizations can design forms to capture specific information while retaining compatibility with Scantron’s automated scanning system.
Overall, Scantron forms are versatile and reliable, capable of handling a wide range of assessment and data collection tasks. Their standardized design, combined with the power of OMR technology, ensures that responses are captured accurately and efficiently, whether for academic, professional, or research purposes.
Advantages of Scantron
Scantron technology offers a wide range of benefits that make it an essential tool in educational institutions, businesses, and research organizations. Its combination of speed, accuracy, and reliability has transformed the way assessments and data collection are conducted.
1. Speed and Efficiency:
One of the most significant advantages of Scantron is its ability to process hundreds or thousands of forms in minutes. Manual grading can be extremely time-consuming, especially for large classes or mass surveys. Scantron automates this process, allowing educators, administrators, and researchers to focus on analysis and decision-making rather than spending hours grading or compiling data.
2. High Accuracy:
By relying on Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) technology, Scantron eliminates much of the human error that occurs during manual grading. Each mark is precisely detected and recorded, ensuring consistent and reliable results. This is particularly important for standardized testing and professional certifications, where accuracy is critical.
3. Standardization:
Scantron provides a uniform assessment format that ensures all respondents are evaluated under the same conditions. This standardization minimizes bias and ensures fairness, particularly in academic and professional testing environments.
4. Cost-Effectiveness:
Although initial setup may require investment in forms and scanners, Scantron ultimately saves time and resources by reducing the need for manual labor. This cost-effectiveness is especially beneficial for institutions and organizations conducting large-scale assessments.
5. Data Analysis and Reporting:
Scantron does more than just grade exams. Its software can generate detailed reports, analyze trends, and summarize survey results, providing valuable insights for educators, administrators, and researchers. This allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate, organized data.
6. Versatility:
From multiple-choice exams to surveys and attendance tracking, Scantron can handle a variety of tasks
In summary, Scantron combines speed, accuracy, and versatility, making it a reliable solution for efficient testing, evaluation, and data collection. Its ability to process large volumes of responses quickly and precisely has made it an indispensable tool across multiple industries.
Disadvantages / Criticisms of Scantron
While Scantron technology offers numerous advantages, it also has certain limitations and has faced criticism in both educational and professional settings. Understanding these drawbacks provides a balanced perspective on its use.
1. Limited Question Types:
Scantron forms are primarily designed for multiple-choice, true/false, and other objective question types. They are not suitable for evaluating essays, short answers, or complex problem-solving skills. This limitation means that assessments relying solely on Scantron may not fully measure critical thinking, creativity, or written communication abilities.
2. Test Anxiety and Pressure:
The standardized, bubble-filled format of Scantron forms can increase anxiety among some students, particularly those who are uncomfortable with high-stakes testing or strict marking procedures. The mechanical nature of the system may also make some learners feel less engaged or restricted in expressing their knowledge.
3. Dependence on Proper Marking:
Accuracy depends on respondents filling in the bubbles correctly and completely. Smudged, incomplete, or stray marks can lead to misread answers and potentially lower scores. While Scantron reduces human grading errors, it is not entirely foolproof and requires careful attention from users.
4. Environmental Concerns:
Traditional Scantron forms are paper-based, leading to significant paper consumption in large-scale testing environments. Although some institutions have moved to digital alternatives, the environmental impact of mass-produced forms remains a concern.
5. Cost and Equipment Requirements:
While cost-effective in the long run, initial investment in Scantron machines, scanners, and forms can be significant for smaller institutions or organizations. Maintenance and software updates may also incur additional expenses.
6. Lack of Flexibility:
Scantron forms follow a rigid structure, limiting their adaptability for innovative assessment methods or personalized testing. This rigidity may not align well with modern pedagogical approaches that emphasize diverse evaluation methods.
Despite these limitations, Scantron remains widely used due to its speed, accuracy, and efficiency, especially in contexts where standardized, objective assessment is a priority. Awareness of its drawbacks allows institutions to complement Scantron with alternative evaluation methods when needed.

Applications of Scantron Today
Scantron technology continues to play a vital role across education, business, and research, adapting to the evolving needs of organizations while maintaining its core purpose of efficient, accurate data collection.
1. Education:
Scantron is most commonly used in schools, colleges, and universities for grading multiple-choice exams, quizzes, and standardized tests. Its ability to process large volumes of answer sheets quickly makes it indispensable in managing classroom assessments, state-level standardized exams, and professional certification tests. Educators also use Scantron to track student performance trends over time, providing insights that inform teaching strategies.
2. Professional Certification and Licensing:
Many professional organizations and licensing bodies rely on Scantron for certification exams. These assessments often involve hundreds or thousands of candidates, making automated grading essential for accuracy, fairness, and efficiency. Examples include accounting certifications, medical licensing exams, and technical skill assessments.
3. Business and Corporate Surveys:
Businesses use Scantron forms to conduct employee evaluations, market research surveys, and customer satisfaction studies. The automated system allows organizations to collect and analyze large datasets quickly, helping management make data-driven decisions. For example, employee feedback collected via Scantron can be summarized to identify areas for improvement or workplace trends.
4. Research and Data Collection:
In research settings, Scantron is used to gather structured survey data efficiently. Academic researchers, social scientists, and market analysts rely on its precision to process large-scale surveys, ensuring that data is accurate and ready for statistical analysis.
5. Administrative and Attendance Tracking:
Scantron forms are also used for attendance monitoring, event registration, and other administrative purposes. By automating data collection, organizations can reduce paperwork, streamline administrative tasks, and maintain accurate records.
Overall, Scantron remains a trusted and widely used tool due to its efficiency, accuracy, and versatility. Its applications extend far beyond education, demonstrating its ability to meet diverse data collection and assessment needs in a variety of professional and organizational contexts.
Conclusion
Scantron technology has revolutionized the way assessments, surveys, and data collection are conducted. By combining machine-readable forms with optical mark recognition (OMR) technology, it provides a system that is fast, accurate, and highly efficient, reducing the time and errors associated with manual grading and data processing.
From its founding in 1972 as a solution to streamline grading in educational institutions, Scantron has grown into a versatile tool used in schools, universities, professional certification exams, businesses, and research organizations. Its ability to handle large volumes of responses quickly and reliably has made it indispensable in environments where accuracy and efficiency are critical.
While Scantron has limitations—such as its restriction to multiple-choice or objective formats and reliance on proper marking—it remains a cornerstone of standardized testing and data collection worldwide. Its enduring success lies in its consistency, speed, and adaptability, making it a trusted choice for educators, administrators, and researchers alike.
As technology continues to evolve, Scantron has also adapted, integrating digital solutions alongside traditional paper-based forms. This ongoing evolution ensures that Scantron remains relevant and continues to meet the needs of modern assessment and data collection, balancing automation, reliability, and accessibility in a variety of contexts.
FAQs
1. What is Scantron?
Scantron is a system that uses machine-readable forms and optical mark recognition (OMR) technology to automate the grading of tests and the collection of survey responses. It is widely used in education, business, and research.
2. How does Scantron’s work?
Respondents fill in bubbles or checkboxes on a Scantron’s form using a pencil. The form is then scanned by a machine that detects the marks, converts them into digital data, and generates results or reports.
3. What types of questions can Scantron’s handle?
Scantron’s is primarily used for multiple-choice, true/false, and other objective questions. It cannot automatically grade essays, short answers, or open-ended questions.
4. Why do Scantron’s forms require a No. 2 pencil?
No. 2 pencils create marks that are dark and consistent enough for the OMR scanner to detect accurately. Pens or lighter pencils may not be read correctly, leading to errors.
5. Where is Scantron’s commonly used?
Scantron’s is widely used in schools, colleges, universities, professional certification exams, corporate surveys, research studies, and attendance tracking.
6. What are the advantages of using Scantron’s?
Scantron’s provides speed, accuracy, standardization, cost-effectiveness, and efficient data analysis, making it ideal for large-scale assessments and surveys.
7. What are the limitations of Scantron’s?
Limitations include restricted question types, reliance on proper marking, environmental impact from paper use, and lack of flexibility for creative or written assessments.
8. Can Scantron’s handle large-scale testing?
Yes. Scantron’s is designed to process hundreds or thousands of forms in minutes, making it perfect for standardized exams, professional certifications, and large surveys.
9. Has Scantron’s evolved with digital technology?
Yes. While traditional Scantron’s forms are paper-based, the company now offers digital scanning solutions and software that allow electronic submission and automated processing.
10. How accurate is Scantron’s grading?
Scantron’s grading is highly accurate because it relies on OMR technology rather than human evaluation. However, accuracy depends on proper filling of the forms, correct scanning, and clean, unmarked bubbles.
Bonus FAQs (Optional):
11. Can Scantron’s forms be reused?
No, most Scantron’s forms are single-use, as the marks made by respondents cannot be erased without affecting scanning accuracy.
12. Who invented Scantron’s?
Scantron’s Corporation was founded in 1972 in the United States, with the goal of automating grading for educational institutions.


